Fan Performance Characteristics of Centrifugal Fans

Centrifugal fan performance characteristics show how well a system moves air. These characteristics are airflow, pressure, efficiency, and power use. Many industries use centrifugal fans to move air against high pressure. They also help collect dust and keep HVAC systems working. High energy efficiency and system reliability depend on matching the fan’s design to its job. The table below shows how changes can make fans work better and last longer:
Performance Characteristic | Quantitative Impact |
|---|---|
Blade angle optimization | 2–8% efficiency gain |
Inlet guide vanes | 7.5% less power |
Flap-angle adjustment | Up to 20.4% savings |
Flow stability | Enhanced reliability |
LONGWELL Centrifugal Fan Blower is known for being reliable and saving energy.
Key Takeaways
Centrifugal fans move air by balancing airflow and static pressure. This helps keep spaces comfortable and systems work well.
Picking the right fan airflow and pressure saves energy. It also makes sure the fan works well and does not waste power.
High-efficiency fans with EC motors use less energy. They run quieter and last longer than regular fans.
Fan performance curves help match fans to what the system needs. This helps avoid problems like noise or weak airflow.
Blade type and impeller size change how a fan handles airflow and pressure. They also affect how much energy the fan uses for different jobs.
Good installation and regular maintenance keep fans working well. This lowers noise and helps fans last longer.
Using smart controls and variable speeds helps fans adjust to changes. This saves even more energy.
Picking fans with good technical support and customization options helps you get the best fit for your needs.

Performance Characteristics
Airflow
CFM
Airflow is very important for a centrifugal fan. CFM means cubic feet per minute. It tells how much air the fan moves each minute. Centrifugal fans use CFM to show airflow rates. A higher CFM means the fan moves more air. This helps with cooling and ventilation.
Picking the right airflow rates is important. The correct CFM keeps the air clean and at the right temperature. A fan with enough airflow keeps air moving in big rooms or factories. If CFM is too low, the room can get hot or stuffy. If CFM is too high, energy is wasted.
Tip: Always look at the CFM rating when picking a centrifugal fan. This helps you choose the right fan for your space and needs.
Measurement
To measure airflow, people use tools like anemometers or pitot tubes. These tools check air speed at the fan’s inlet or outlet. Technicians multiply the speed by the area to get the volume flow rate. Manufacturers give fan performance curves. These show airflow at different pressures and speeds.
LONGWELL Centrifugal Fan Blower uses smart electronics and EC motors. These fans give exact airflow control. They can change airflow rates for different needs. Smart controls keep CFM steady, even if system conditions change.
Why airflow capacity matters in centrifugal fans:
Good airflow keeps air fresh and people comfortable.
The right size saves energy.
It works well with ductwork.
Reliable fans last longer and break less.
Static Pressure
Definition
Static pressure is the force air pushes on duct walls as it moves. In centrifugal fans, static pressure shows the resistance the fan must beat. The fan pushes air through filters, ducts, or vents. When static pressure goes up, airflow goes down. This opposite link is important for fan performance.
Static pressure is measured in inches of water gauge. Tools like pitot tubes and anemometers help measure it. They check air speed and pressure at different spots. The real airflow and static pressure depend on where the fan curve and system curve meet.
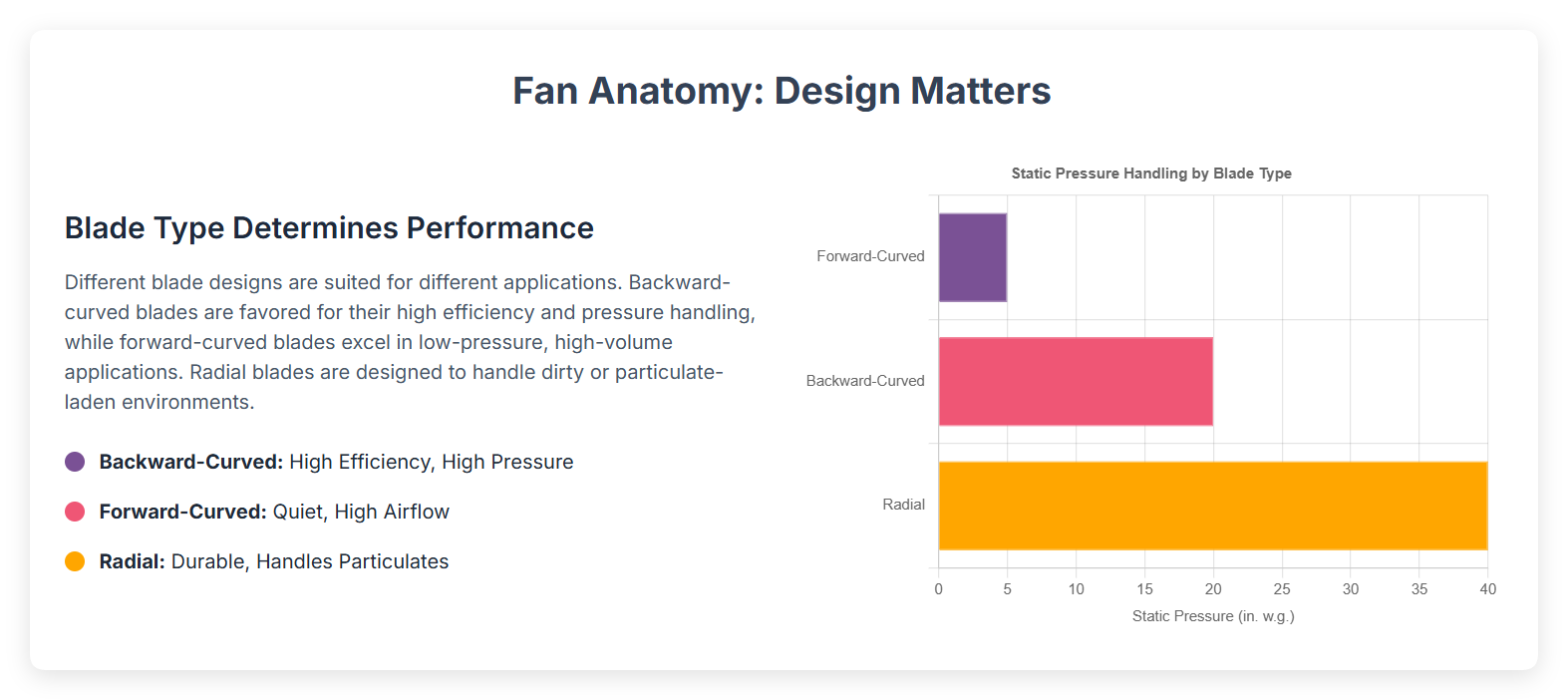
Fan Type | Typical Static Pressure Range (in. w.g.) | Typical Application Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
Forward Curved | 3 to 5 | Large air volumes at low pressure, light-gauge construction |
5 to 20 | Moderate pressures, high static efficiency, clean air applications | |
Radial | Up to 40 | High static pressures, suitable for dirty or dusty environments |
System Impact
Static pressure changes how well a centrifugal fan works. High static pressure makes the fan work harder. This can lower airflow rates. More bends, filters, or long ducts raise static pressure. Designers must figure out static pressure to pick the right fan size.
In commercial HVAC, knowing static pressure helps keep fans efficient. Too much safety margin wastes energy and money. LONGWELL Centrifugal Fan Blower can handle many static pressures. This makes it good for many HVAC and ventilation jobs.
Efficiency
Factors
Fan efficiency shows how well a centrifugal fan turns electricity into airflow. Many things affect fan efficiency:
Blade shape, number, and angle.
Bionic designs, like edges and ridges that copy owl wings.
Motor technology, especially EC motors.
Designers use these ideas to cut turbulence and make smooth airflow. This makes the fan work better and boosts efficiency. AMCA 210 is a standard to measure and compare efficiency.
Importance
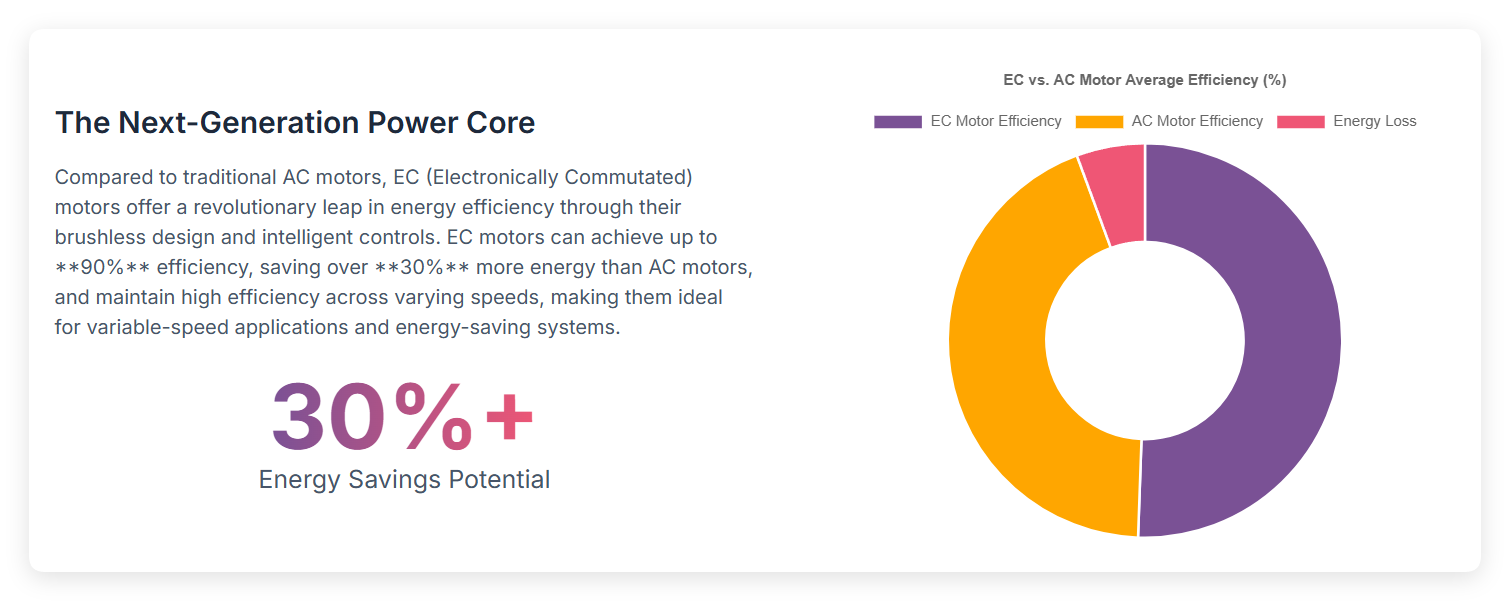
High fan efficiency means the fan uses less power for the same airflow. EC motors in centrifugal fans can reach up to 90% efficiency. They use over 30% less power than AC motors. EC motors also keep efficiency high at different speeds. This is good for systems that change speed.
Motor Type | Average Efficiency Range (%) |
|---|---|
AC Motors | 70 - 88 |
EC Motors | 80 - 90 |
LONGWELL Centrifugal Fan Blower uses EC motors and smart controls. This helps the fan work efficiently. It lowers energy costs and gives better airflow control. Efficient fans are quieter and help HVAC systems last longer.
Note: Picking a centrifugal fan with high efficiency saves energy and makes the system more reliable.
Power Consumption
BHP
Brake horsepower (BHP) tells us how much power a fan needs. Engineers use BHP to see how much energy the motor must give. BHP shows the work the motor does before any energy is lost. If the fan pushes air harder or moves more air, BHP gets higher. LONGWELL Centrifugal Fan Blower uses special EC motors. These motors work well and keep BHP low for the same airflow. This saves energy and cuts costs. Fans with smart controls can change speed and power use. This makes them work better in different situations.
Note: Picking a fan with the right BHP stops wasted energy. It also helps the system work well.
Calculation
Engineers use a simple formula to find out how much power a fan uses. The formula is:
Power (W) = Total Pressure (Pa) × Airflow (m³/s) ÷ Fan Efficiency
To get a better answer, they add motor and belt efficiency:
Power (W) = Total Pressure (Pa) × Airflow (m³/s) ÷ (Fan Efficiency × Belt Efficiency × Motor Efficiency)
Fan efficiency depends on how the fan is made. EC motors in LONGWELL fans can be up to 90% efficient. Motor efficiency changes with size. Small motors (1 kW) are about 40% efficient. Bigger motors (10 kW) are 87% efficient. Very big motors (100 kW) can be 92% efficient.
Motor Power | Typical Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|
1 kW | 40 |
10 kW | 87 |
100 kW | 92 |
Backward-curved blades help fans use less power. These blades lower friction and turbulence. This means the fan needs less energy for the same job. This design also keeps power use from going up too fast when airflow rises.
Fans in large buildings run all year. In air handling units, fans can use up to 85% of the system’s energy. Lowering air speed in ducts and making fans more efficient can cut power use by up to 87%. Using good fans like LONGWELL Centrifugal Fan Blower saves money and energy.
Fans often run all year, even if other systems are off.
Lowering system pressure and airflow can save a lot of power.
Efficient fans and smart controls help save money in big buildings.
Tip: Always look at the fan’s efficiency and power ratings. Fans that use less energy help lower your bills.
Fan Performance Curves
Understanding Curves
Fan performance curves help people see how a centrifugal fan works. These curves show how airflow and static pressure are connected. On a graph, airflow goes side to side. Static pressure goes up and down. The curve is not a straight line. When static pressure gets higher, airflow gets lower. The change is not always the same. The curve also has special parts like the stall range. In this range, one static pressure can match more than one airflow. This can cause noise or shaking. Looking at the curve helps people guess what will happen if they add filters or change ducts. Changing blade pitch angles can help keep airflow steady. Fan performance curves help people pick the right fan and keep things working well.
Tip: Always look at the fan performance curve before you pick a fan. This helps you avoid problems and keeps airflow steady.
Airflow vs. Pressure
The most common curves for centrifugal fans are airflow versus static pressure and airflow versus brake horsepower. The airflow versus static pressure curve goes down. The most airflow happens when static pressure is zero. This is called free delivery. When static pressure is highest, airflow is zero. This is called shut off. The curve has an unstable stall area at low airflow and high static pressure. Working in this area can cause shaking, noise, and damage. The brake horsepower curve goes up. It shows that power use gets higher as airflow gets higher. To be safe and work well, the fan should run in the stable part of the curve, away from the stall area.
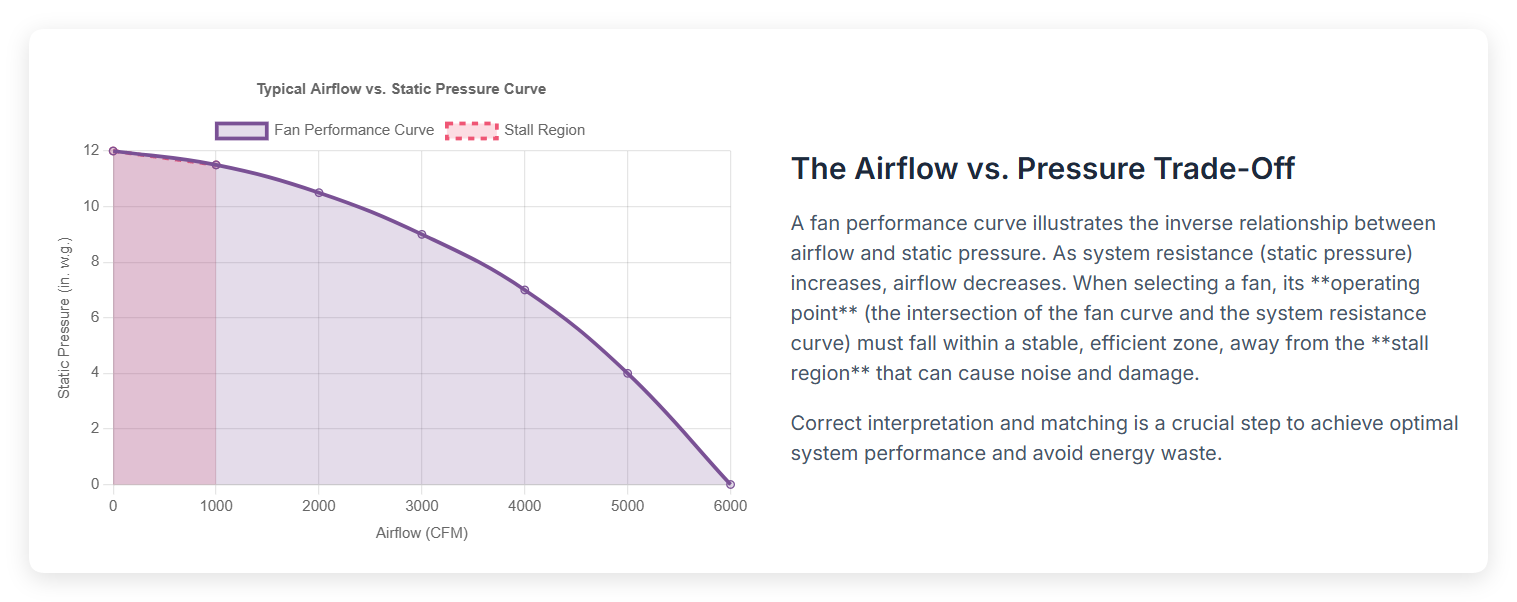
LONGWELL Centrifugal Fan Blower uses smart design and EC motors. This helps the fan stay in the stable part of the curve. The fan stays quiet and works well, even when things change.
Curve Interpretation
Reading a fan performance curve means finding where the fan meets the system’s needs. Every system has its own curve. This curve shows how pressure drop changes with airflow. The operating point is where the two curves cross. Things like ducts, filters, or dampers change the system curve. If resistance goes up, the operating point moves to less airflow and more static pressure. If resistance goes down, airflow goes up and static pressure goes down. Changes in resistance can push the fan into unstable areas. This can cause noise and make the fan break sooner.
The PQ curve shows how static pressure and airflow rate are connected.
Each system has its own curve, which changes with resistance.
The real operating point is where the two curves cross.
Resistance can change over time, like when filters get dirty.
Picking a fan should keep it working in the stable part of the curve.
LONGWELL gives detailed fan performance curves for every model. These curves help people match fans to their systems and avoid problems. Using LONGWELL data helps people pick fans that give steady airflow and save energy in real life.
Centrifugal Fan Design

Blade Types
The blade type changes how air moves and how much energy is used. Each blade style works best for certain jobs and systems.
Forward-Curved
Forward-curved blades bend the same way the fan spins. These blades move a lot of air and are not very loud. They work well in places with low pressure and lots of air, like HVAC and electronics cooling. Forward-curved fans cost less and are quiet. But they do not work as well when pressure is high.
Backward-Curved
Backward-curved blades bend away from the way the fan spins. This shape gives better control of airflow and uses less energy. Backward-curved fans work well when pressure is high. They are good for factories, data centers, and clean air places. These fans can be louder than forward-curved fans. New designs help make them quieter. LONGWELL uses backward-curved blades and EC motors to save energy and work better.
Radial
Radial blades stick straight out from the center. These blades are good for moving dirty air and working against strong resistance. Radial fans are used in dusty places and for moving materials. They are not as efficient as backward-curved fans and can be louder. But they work well in tough jobs.
Tip: Pick the blade type that fits your airflow and pressure needs.
Blade Type | Blade Orientation | Airflow Characteristics | Efficiency and Pressure Handling | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Forward Curved | Curves in direction of rotation | High airflow, increased turbulence | Lower efficiency at high pressures; limited static pressure | HVAC, electronics cooling |
Backward Curved | Curves away from rotation direction | Better airflow control, reduced turbulence | Higher efficiency; performs well at higher static pressures | Industrial, data centers |
Radial | Perpendicular to rotation direction | Handles high resistance, particulate-laden air | Less efficient; reliable in harsh environments | Dusty or contaminated air |
Impeller Size
Impeller size changes how much air the fan can move. It also changes how much pressure the fan can make. A bigger impeller spins faster at the edge and pushes air harder. This means more airflow and more pressure. Big impellers are best for jobs that need high pressure, like dust collectors or long ducts. But if the impeller is too big, it can make the motor work too hard. The impeller size must match the motor so the fan is safe and works well.
Aspect | Explanation |
|---|---|
Impeller Diameter | Larger diameter increases tip speed and centrifugal force, enhancing pressure and airflow. |
Application Preference | Larger impellers are preferred for high static pressure needs (e.g., dust collectors, long ducts). |
Design Caution | Oversized impellers may cause motor overload; matching impeller size with motor capacity is crucial. |
LONGWELL has impellers from 133mm to 630mm. This lets people pick the right size for their airflow and pressure needs.
Motor Technology
Motor technology is important for how well the fan works. EC motors use brushless DC parts and special controls. These motors can change speed exactly and are very efficient, even when not running at full power. EC motors waste less energy and need less fixing. Built-in electronics let you control the fan with PWM, analog signals, or Modbus. This makes it easy to match airflow to what is needed and saves energy.
LONGWELL fans use advanced EC motors and backward-curved impellers. These fans can change speed and use smart controls. The brushless design makes them quiet and last a long time. LONGWELL lets customers pick motor types, speed controls, and voltage. You can also get features like over-voltage protection, special coatings, and special impeller designs.
Note: Picking the right motor technology helps save energy and makes the system more reliable.
LONGWELL can make fans for special jobs. You can choose different materials, impeller sizes, motor types, and controls. These choices make LONGWELL fans good for HVAC, cleanrooms, data centers, and factories.
Real-World Factors
Installation
How you install a centrifugal fan really matters. Good installation helps the fan give the right airflow and pressure. Bad installation can cause problems like noise and weak performance. Some mistakes are elbows too close to the fan or sharp duct changes. Dampers in the wrong place also cause trouble. These mistakes block airflow and lower pressure. The fan might not work as planned. This can waste energy and make more noise.
Installers should set up the fan like it was tested.
Turning vanes and smooth ducts help airflow stay steady.
Do not let air blow out freely or change duct size quickly.
If space is small, add system effect losses to resistance.
Looking at the fan can show problems like wrong speed or rotation.
Fixing bad installation costs more than doing it right first. Good installation helps airflow and keeps the system working well.
System Resistance
System resistance is the force the fan must beat to move air. This happens in ducts, filters, and other parts. Centrifugal fans do better with high resistance than other fans. High resistance makes the fan work harder. This changes how much air it moves and how much energy it uses. The impeller and fan housing design help keep airflow steady, even if resistance changes.
Static pressure tells how much resistance is in the system.
Long or tight ducts make resistance higher.
The right impeller blade helps the fan handle resistance.
Good care helps the fan work well, even if resistance changes.
System resistance changes power use and airflow. Picking the right fan and keeping things clean helps the fan work well.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance keeps centrifugal fans working well for a long time. Simple jobs like cleaning and oiling stop problems. Checking for wear helps catch trouble early. Balanced impellers and checking for shaking help the fan last longer. Changing old parts and making sure things are tight keeps the fan running smoothly.
Regular checks find problems before they get big.
Oiling and cleaning stop dust and overheating.
Balanced fans avoid extra stress and early breakdowns.
Fixing and changing parts on time stops bigger issues.
Training workers helps them use and care for the fan.
These steps cut downtime, save energy, and help the fan last longer. LONGWELL gives full technical help and a standard warranty. Their team helps from the first talk to installation and care. Customers can get help any time, day or night. LONGWELL also helps with special designs for different needs. This strong support and warranty help customers feel safe and trust their fans.
Centrifugal Fan Selection

Application Needs
Picking centrifugal fans starts with knowing what the job is. Engineers check a few important things before choosing:
Volumetric flow rate (CFM): The fan must move enough air for the space.
Fan static pressure: The fan needs to push air past ducts and filters.
Inlet air density: Temperature, height, and moisture change how much air moves.
Intended fan duty: Some fans work with clean air, others handle dust or wet air.
Engineers also think about noise, what the fan is made of, and how long it will last. They look at details and see if the company makes good products. Experts help and fans get tested in real places to make sure they work. LONGWELL Centrifugal Fan Blower lets people pick size, blade material, voltage, and how to mount it. The company allows small orders and ships quickly, which helps with special projects.
Tip: Always match the fan’s airflow and pressure ratings to your system’s needs for the best results.
Using Performance Data
Engineers use fan performance curves to pick the right centrifugal fan. These curves show how airflow and static pressure change together. They draw the system resistance curve and the fan curve to find the operating point. This point shows if the fan can give the airflow and pressure needed.
Performance curves help engineers see if the fan will work well in real life. They also use the curves to check how strong the motor must be and how fast the fan should spin. For example, a fan may need a certain brake horsepower to reach the airflow at a set pressure. LONGWELL gives detailed fan performance curves for every model. This helps people pick the right fan and avoid problems like noise or weak airflow.
Note: Using fan performance data and curves helps the fan meet system needs and work well.
Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency is important when picking a fan. Engineers choose centrifugal fans that use less power and save money. They look for fans with good blade shapes and advanced motors. Fans with variable-speed controls can change speed to match what is needed, so energy is not wasted.
Regular care and checking help fans stay efficient. Smart controls, like sensors, let fans change when things in the system change. LONGWELL Centrifugal Fan Blower uses EC motors and smart controls to save energy. The company gives strong technical help and worldwide service, so customers get reliable and efficient systems.
Strategy for Energy Efficiency | Benefit |
|---|---|
Optimized blade design | Less turbulence, more airflow |
Variable-speed control | Lower power use |
Smart monitoring | Maintains top fan efficiency |
High-efficiency motors | Saves energy, reduces costs |
🌱 Picking fans with high energy efficiency helps the planet and saves money over time.
Knowing how centrifugal fans work helps engineers pick the best fan. Measuring airflow, pressure, and power helps make better systems. This also saves energy. Things like resistance and how you install the fan change how it works.
Picking fans that are efficient and reliable, like LONGWELL fans, gives good performance and support for a long time.
Remember these key ideas:
Always look at fan curves and what your system needs.
Choose fans that are efficient, reliable, and have good technical help for the best results.
FAQ
What does CFM mean in centrifugal fans?
CFM means cubic feet per minute. It tells how much air a fan moves each minute. If the CFM is higher, the fan moves more air. This helps cool rooms and keeps air fresh.
How does static pressure affect fan performance?
Static pressure is the force the fan must push against. If static pressure is high, the fan has to work harder. This can make the fan move less air. Designers use static pressure to pick the right fan for each job.
Why is fan efficiency important?
Fan efficiency shows how well a fan uses electricity to move air. High efficiency saves energy and money. Efficient fans are also quieter and last longer.
What is a fan performance curve?
A fan performance curve is a graph. It shows how airflow and static pressure change together. Engineers use this graph to find the best way for a fan to work in a system.
How do EC motors improve centrifugal fans?
EC motors have special electronics to control speed. They help the fan use less energy and make less noise. These motors also last longer than regular motors.
What maintenance does a centrifugal fan need?
Fans need regular cleaning and oiling. Checking for worn parts helps stop problems early. Balanced impellers and tight parts keep the fan running well. Good maintenance helps the fan last longer.
Can LONGWELL Centrifugal Fan Blower be customized?
LONGWELL lets you pick different impeller sizes, motor types, and controls. Customers can choose what they need for their own jobs.
Where are centrifugal fans used?
Centrifugal fans are used in HVAC, factories, cleanrooms, and farms. They help move air, control temperature, and get rid of dust or fumes.
See Also
Ways Longwell Centrifugal Fans Deliver Outstanding Energy Efficiency
The Importance Of Centrifugal Fans In HVAC And Industry
Selecting The Best Centrifugal Fan For Your 2025 Needs
Complete Guide To Forward Curved Fans In Modern HVAC
Benefits Of LONGWELL Forward Fans For Optimal Energy Savings
